A new report from Dodge Data & Analytics breaks down how digital transformation is causing significant changes in the construction industry right now.
One section of the report, “Digital Transformation of the Design and Construction Industry,” describes the growing use of BIM and related emerging technologies by construction and design companies — as well as how far these businesses are in their digital transformations.
The report finds that BIM users tend to be ahead of the curve technologically compared to non-users — and that BIM use is a strong predictor of whether or not an organization has adopted new digital construction and design tools. Organizations that self-report “high BIM intensity” — defined as employing BIM tech for at least 75% of projects — are also more likely to have adopted emerging construction technologies.
Only 3% of all BIM users and just 1% of high-intensity BIM users reported that they had not started their digital transformation journey yet, for example, compared to 18% of non-BIM users.
High BIM intensity organizations were also the most likely among both users and non-users to report their organization was “approaching the goal” or had “already achieved the goal” of digital transformation.
How BIM Is Related to the Use of Emerging Technologies
In addition to surveying BIM users and non-users on the stage of their digital transformation, Dodge researchers also asked about the adoption of 16 emerging technologies — including novel digital design tools, innovative construction methods, smart building technology, emerging job site tech, and new means of data sharing.
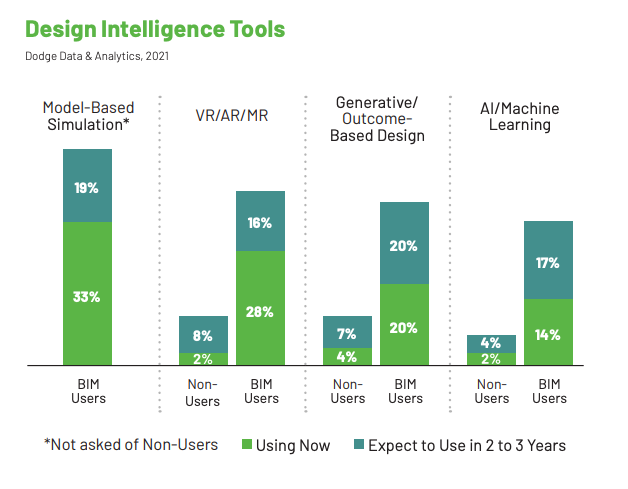
In general, BIM users were significantly more likely to have adopted novel construction technologies than non-users. For example, 26% of BIM adoptees currently use or expect to use IoT in the next two to three years, compared to 6% of use or expected use by businesses that don’t leverage BIM. Similarly, 44% of BIM users currently use or expect to use AR, VR, or MR, compared to just 10% of non-users.
The study’s authors predict that because non-users consistently lag behind users in terms of technology adoption, existing gaps in use are likely to expand in the future.
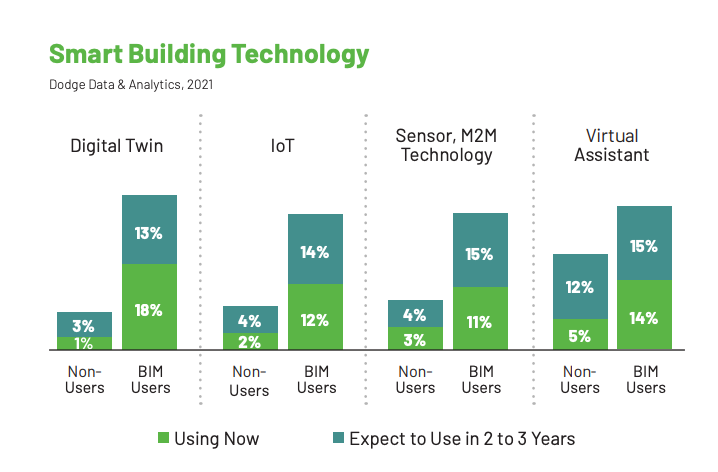
Some technologies are outliers. Roughly the same number of BIM non-users and users have adopted cloud computing, for example, and both virtual assistants and remote computing technologies are only slightly less popular among non-users compared to users.
Trends in Digital Solution Use in Construction
The survey also tells us which tools construction companies are adopting right now and which tools continue to lag behind, even among businesses investing heavily in digital transformation.
Of all tech considered to be an emerging technology by Dodge, cloud computing was the most widely adopted among both BIM users and non-users. The second most-adopted technology was reality capture among non-users and model-based simulation among users.
There are also certain technologies that have attracted very few non-BIM users, like design for manufacturing and assembly (DFMA), with 7% adoption among non-users, and digital twins, with just 4% adoption.
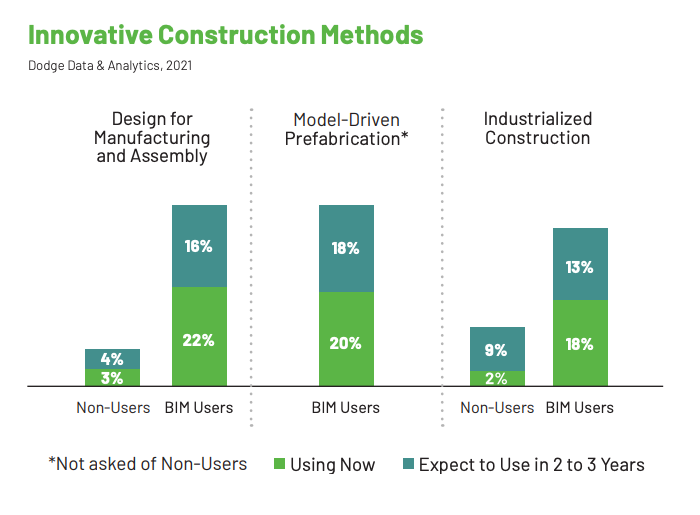
In general, technologies that work best when used alongside other digital solutions — like IoT, DFMA, and digital twins — were less likely to be adopted by organizations that hadn’t yet invested in BIM.






